[자료구조] 스택(Stack) by JS
📄 스택(Stack)
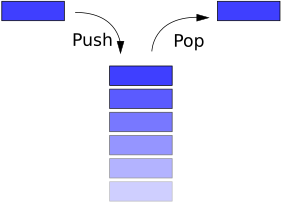
스택은 LILF(Last In First out) 원칙을 따르는 선형 자료구조입니다.
마지막에 삽입된 데이터가 가장 먼저 삭제되는 구조로, 접시를 쌓아올리는 것과 비슷합니다.
▪︎ 주요 특징
- 후입선출 구조
- TOP이라는 한쪽 끝에서만 삽입, 삭제 연산 수행
- 순차적인 접근만 가능 (중간 요소에 직접 접근 불가)
▪︎ 기본 연산
- push: 스택의 맨 위에 데이터 삽입
- pop: 스택의 맨 위 데이터 제거 및 반환
- TOP(Peek): 스택의 맨 위 데이터 확인
- isEmpty: 스택이 비었는지 확인
- Size: 스택에 저장된 데이터의 개수 반환
▪︎ 구현 방법
1. 배열 기반 구현: 고정 크기, 빠른 접근
class ArrayStack {
constructor(maxSize = 1000) {
this.items = [];
this.maxSize = maxSize;
}
// 스택에 원소 추가
push(element) {
if (this.items.length >= this.maxSize) {
throw new Error("Stack Overflow");
}
this.items.push(element);
}
// 스택에서 원소 제거 및 반환
pop() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
throw new Error("Stack Underflow");
}
return this.items.pop();
}
// 스택의 맨 위 원소 확인
peek() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
throw new Error("Stack is empty");
}
return this.items[this.items.length - 1];
}
// 스택이 비어있는지 확인
isEmpty() {
return this.items.length === 0;
}
// 스택의 크기 반환
size() {
return this.items.length;
}
// 스택 출력
display() {
console.log("Stack:", this.items);
}
}
연결리스트 기반 구현: 동적 크기, 메모리 효율적
- 연결리스트는 자바스크립트에서 기본으로 제공하지 않아 직접 구현해서 사용해야 합니다.
/**
* 연결리스트 기반 스택 구현
*/
class Node {
constructor(data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
class LinkedListStack {
constructor() {
this.top = null;
this.count = 0;
}
// 스택에 원소 추가
push(data) {
const newNode = new Node(data);
newNode.next = this.top;
this.top = newNode;
this.count++;
}
// 스택에서 원소 제거 및 반환
pop() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
throw new Error("Stack Underflow");
}
const data = this.top.data;
this.top = this.top.next;
this.count--;
return data;
}
// 스택의 맨 위 원소 확인
peek() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
throw new Error("Stack is empty");
}
return this.top.data;
}
// 스택이 비어있는지 확인
isEmpty() {
return this.top === null;
}
// 스택의 크기 반환
size() {
return this.count;
}
// 스택 출력
display() {
const elements = [];
let current = this.top;
while (current) {
elements.push(current.data);
current = current.next;
}
console.log("Stack:", elements);
}
}
// 사용 예제
function stackExample() {
console.log("=== 배열 기반 스택 ===");
const arrayStack = new ArrayStack();
arrayStack.push(1);
arrayStack.push(2);
arrayStack.push(3);
arrayStack.display(); // [1, 2, 3]
console.log("Pop:", arrayStack.pop()); // 3
console.log("Peek:", arrayStack.peek()); // 2
console.log("Size:", arrayStack.size()); // 2
console.log("\n=== 연결리스트 기반 스택 ===");
const linkedStack = new LinkedListStack();
linkedStack.push('A');
linkedStack.push('B');
linkedStack.push('C');
linkedStack.display(); // ['C', 'B', 'A']
console.log("Pop:", linkedStack.pop()); // C
console.log("Peek:", linkedStack.peek()); // B
console.log("Size:", linkedStack.size()); // 2
}
출처
- 그림으로 배우는 자료구조와 알고리즘
💬 최신 댓글